|
Case Report
Prosthetic rehabilitation using a cone morse dental implant and xenogen biomaterial in an aesthetic area: A case report
1 Department of Implantology, Faculty of Dentistry, Portuguese Catholic University, Lisboa, Portugal
2 Department of Implantology, Faculty of Dentistry, São Leopoldo Mandic University, Brasilia, Brazil
3 Department of Implantology, Faculty of Dentistry, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
4 Department of Biology (IBRAG), Faculty of Medicine, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
5 Department of Orthodontic, Faculty of Dentistry, State University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
Address correspondence to:
Igor da Silva Brum
Department of Implantology, Faculty of Dentistry, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro,
Brazil
Message to Corresponding Author
Article ID: 100033Z07JL2020
Access full text article on other devices

Access PDF of article on other devices

How to cite this article
Lopes JCA, Salviano SH, Carvalho MA, de Carvalho JJ, Devita RL, Lucas PDR, Brum IDS. Prosthetic rehabilitation using a cone morse dental implant and xenogen biomaterial in an aesthetic area: A case report. J Case Rep Images Dent 2020;6: 100033Z07JL2020.ABSTRACT
Introduction: With the worldwide growth of aesthetic treatments, oral rehabilitation has gained new vestments, where only the implant placement and their functional activation are not enough. It is necessary to do a whole three-dimensional planning, taking into account the remaining bone, possibilities of grafting before, during, or after the implant placement, the final prosthesis and especially the pink tissues handling and aesthetic.
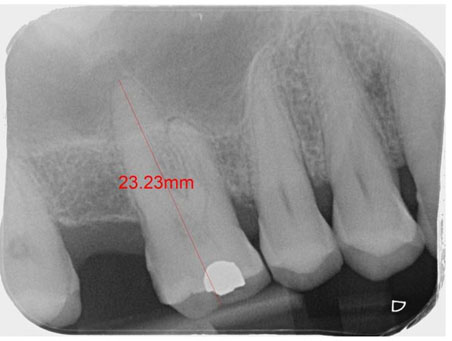
Case Report: In this case report, we can assess the loss of the dental element 22, which had a broad root lesion with almost total loss of the buccal wall. The extraction of this element was planned and a cone morse dental implant (Systhex® Avantt model, Curitiba, Brazil) was placed and grafted with a xenogenous biomaterial (Bio Oss®, Geistlich Pharm, Switzerland). After 9 months, it was reopened and the provisional prosthesis was made for tissue management. After this, a porcelain crown was cemented.
Conclusion: We can conclude that when planning correctly and using a cone morse dental implant, the prosthetic result and the surrounding soft tissues behave more favorably for an aesthetic format more compatible with current standards.
Keywords: Aesthetic, Biomaterial, Cone morse, Dental implants, Pink aesthetics
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
Author Contributions:
João Carlos Amorim Lopes - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Drafting the article, Final approval of the version to be published
Saulo Henrique Salviano - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Drafting the article, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Marco Antônio Carvalho - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Jorge José de Carvalho - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Drafting the article, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Renan Lana Devita - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Analysis of data, Drafting the article, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Pablo Dallario Ramalho Lucas - Acquisition of data, Analysis of data, Drafting the article, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Igor da Silva Brum - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Drafting the article, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Guaranter of SubmissionThe corresponding author is the guarantor of submission.
Source of SupportNone
Consent StatementWritten informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this article.
Data AvailabilityAll relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Conflict of InterestAuthors declare no conflict of interest.
Copyright© 2020 João Carlos Amorim Lopes et al. This article is distributed under the terms of Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium provided the original author(s) and original publisher are properly credited. Please see the copyright policy on the journal website for more information.