|
Case Report
Localized actinomycosis at gingiva
1 Department of Otolaryngology, Ogaki Tokushukai Hospital, 6-85-1, Hayashi-machi, Ogaki City, Gifu 503-0015, Japan
2 Department of Otolaryngology, Gifu University Hospital, 1-1 Yanagido, Gifu City, Gifu 501-1194, Japan
3 Department of Internal Medicine, Infection Control Team, Ogaki Tokushukai Hospital, 6-85-1, Hayashi-machi, Ogaki City, Gifu 503-0015, Japan
4 Department of Dental and Oral Surgery, Ogaki Tokushukai Hospital, 6-85-1, Hayashi-machi, Ogaki City, Gifu 503-0015, Japan
5 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Ogaki Tokushukai Hospital, 6-85-1, Hayashimachi, Ogaki City, Gifu 503-0015, Japan
Address correspondence to:
Mitsuhiro Aoki
Department of Otolaryngology, Ogaki Tokushukai Hospital, 6-85-1, Hayashimachi, Ogaki City, Gifu 503-0015,
Japan
Message to Corresponding Author
Article ID: 100043Z07MA2022
Access full text article on other devices

Access PDF of article on other devices

How to cite this article
Aoki M, Okuda H, Nogami Y, Jinno Y, Mori H. Localized actinomycosis at gingiva. J Case Rep Images Dent 2022;8(2):1–5.ABSTRACT
Introduction: Gingival actinomycosis is a rare disease caused by Actinomyces israelii in the oral cavity.
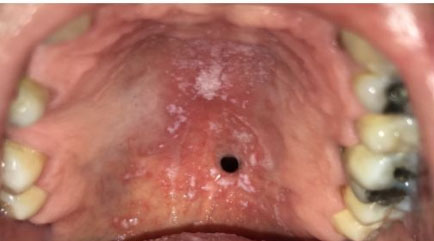
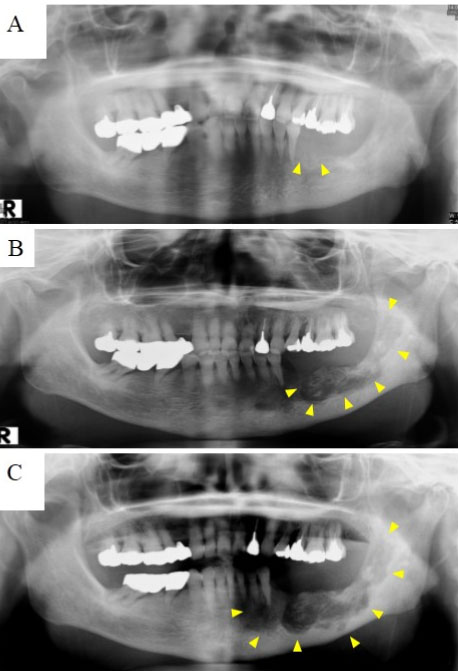
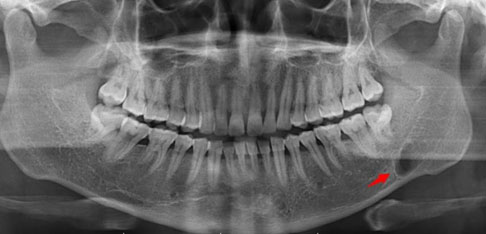
Case Report: A 42-year-old healthy man without underlying diseases or any teeth troubles suffered from severe pain in the gingival of the right mandibular bone for three weeks. The intraoral inspection revealed a well-defined elastic hard mass with a size less than 10 mm on the medial side of the right mandibular gingiva. The histopathological examination proved that the bacterial druse with radial structure invaded the bone margin widely and proliferated in some places of the bone. After removing the mass and scraping off the around bone, followed by two month-oral use of Amoxicillin (AMPC:1500 mg/day), his complaints and the gingival tissue have been entirely resolved.
Conclusion: The morphological features of the growth of actinomyces in the bone margin by the limited lesion of actinomycosis at the gingiva have not ever been reported. Even localized actinomycosis at gingiva should be adequately treated.
Keywords: Actinomycosis, Amoxicillin, Druse, Gingiva
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
Author Contributions:
Mitsuhiro Aoki - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis of data, Interpretation of data, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Hiroshi Okuda - Acquisition of data, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Yashiro Nogami - Interpretation of data, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Yosuke Jinno - Interpretation of data, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Hideki Mori - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Analysis of data, Interpretation of data, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Guaranter of SubmissionThe corresponding author is the guarantor of submission.
Source of SupportNone
Consent StatementWe obtained the informed consent from the patient by writing.
Data AvailabilityAll relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Conflict of InterestAuthors declare no conflict of interest.
Copyright© 2022 Mitsuhiro Aoki et al. This article is distributed under the terms of Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium provided the original author(s) and original publisher are properly credited. Please see the copyright policy on the journal website for more information.